Last time we discussed the “spatial gradient” or “3-gradient”, and here we follow up with two examples. Recall from before that a scalar field ![]() has gradient
has gradient ![]() , and the part of this which is orthogonal to an observer 4-velocity
, and the part of this which is orthogonal to an observer 4-velocity ![]() is, as a vector:
is, as a vector:
![]()
This direction has the greatest increase of ![]() , for any vector in
, for any vector in ![]() ’s 3-space (that is, orthogonal to
’s 3-space (that is, orthogonal to ![]() ), per length of the vector.
), per length of the vector.
As an example, suppose the 4-gradient vector ![]() is a null, future-pointing vector. It can be decomposed
is a null, future-pointing vector. It can be decomposed ![]() , where
, where ![]() , and
, and ![]() is a unit spatial vector orthogonal to
is a unit spatial vector orthogonal to ![]() . Physically, this gradient may be interpreted as a null wave or photon, which the observer determines to have energy (or related quantity, such as frequency)
. Physically, this gradient may be interpreted as a null wave or photon, which the observer determines to have energy (or related quantity, such as frequency) ![]() , and to move in the spatial direction
, and to move in the spatial direction ![]() . The 3-gradient vector is
. The 3-gradient vector is ![]() , hence the direction of relative velocity also has the steepest increase of
, hence the direction of relative velocity also has the steepest increase of ![]() , within the observer’s 3-space.
, within the observer’s 3-space.
Suppose now ![]() is a unit, timelike, future-pointing vector, so that we may interpret it as the 4-velocity
is a unit, timelike, future-pointing vector, so that we may interpret it as the 4-velocity ![]() of a second observer. Then
of a second observer. Then ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the Lorentz factor between the pair. But we also have the “relative velocity” decomposition
is the Lorentz factor between the pair. But we also have the “relative velocity” decomposition ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the relative velocity of
is the relative velocity of ![]() as determined in
as determined in ![]() ’s frame, as I discussed previously. Combining these,
’s frame, as I discussed previously. Combining these, ![]() . Hence within the observer’s 3-space,
. Hence within the observer’s 3-space, ![]() again increases most sharply in the direction of the relative velocity.
again increases most sharply in the direction of the relative velocity.
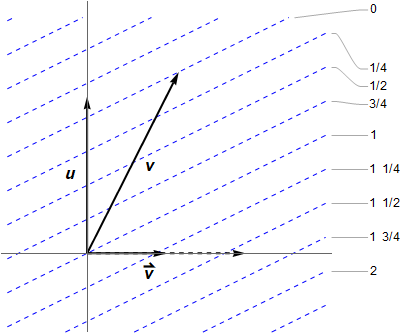
 ‘s perspective. The timelike 1-form
‘s perspective. The timelike 1-form  is suggested by dotted blue lines, given at intervals of 1/4 for more resolution. These are orthogonal to the vector
is suggested by dotted blue lines, given at intervals of 1/4 for more resolution. These are orthogonal to the vector  , in the Lorentzian sense.
, in the Lorentzian sense.The figure shows the single tangent space — think of this as the linearisation of what is happening locally over the manifold itself. The hyperplanes are numbered by ![]() , where only the differences between them are relevant, as an overall constant was not specified. Observe
, where only the differences between them are relevant, as an overall constant was not specified. Observe ![]() crosses four of them, spanning an interval
crosses four of them, spanning an interval ![]() , so
, so ![]() is the negative of
is the negative of ![]() ’s proper time; see a previous post for more background. In both our examples, the scalar decreases towards the future (or can vanish in the null case), even though the gradient vectors are future-pointing. That is, the gradient vectors actually point “down” the slope! This quirk is due to our −+++ metric signature, and would apply to spacelike gradients if +−−− were used instead. This really hurt my brain, until I drew the diagram. 🙁
’s proper time; see a previous post for more background. In both our examples, the scalar decreases towards the future (or can vanish in the null case), even though the gradient vectors are future-pointing. That is, the gradient vectors actually point “down” the slope! This quirk is due to our −+++ metric signature, and would apply to spacelike gradients if +−−− were used instead. This really hurt my brain, until I drew the diagram. 🙁
To construct it, consider the action of ![]() on the axes. The horizontal axis is the relative velocity direction, with unit vector
on the axes. The horizontal axis is the relative velocity direction, with unit vector ![]() . One can show
. One can show ![]() . Also
. Also ![]() , but I find it easier to think of:
, but I find it easier to think of: ![]() . These give the number of hyperplanes crossed by the unit axes vectors, then you can literally “connect the dots” since the 1-form is linear. In the figure
. These give the number of hyperplanes crossed by the unit axes vectors, then you can literally “connect the dots” since the 1-form is linear. In the figure ![]() , so
, so ![]() . (As for the 3-gradient, it vanishes in the
. (As for the 3-gradient, it vanishes in the ![]() direction, hence
direction, hence ![]() must cross no contours of
must cross no contours of ![]() . It would be drawn as vertical lines, with corresponding vector pointing to the right.)
. It would be drawn as vertical lines, with corresponding vector pointing to the right.)
Most of our discussion applies to arbitrary 1-forms, not just gradients which are termed exact 1-forms. I derived the work here independently, but the literature contains some similar material. It turns out Jantzen, Carini & Bini 1992  §2 explicitly define the “spatial gradient”, as they most appropriately call it. A few textbooks discuss scalar waves, for which the 3-gradient vector is the wave 3-vector, which is orthogonal to the wavefronts within a given frame, as discussed shortly.
§2 explicitly define the “spatial gradient”, as they most appropriately call it. A few textbooks discuss scalar waves, for which the 3-gradient vector is the wave 3-vector, which is orthogonal to the wavefronts within a given frame, as discussed shortly.